 |
| Michigan lily flowering in mid-July in Hennepin County, Minnesota. |
This lone Michigan lily (Lilium michiganense), barely out of reach of the ditch mower and surrounded by invasive reed canary grass (Phalaris arundinacea), grows at the edge of a wetland. That’s typical for this native perennial, which is also found along streambanks and shores and in wet meadows, prairies, bogs and woodland edges and openings.
Michigan lily looks much like Turk’s cap lily (Lilium superbum),
another native that grows in the same habitats farther south. In fact, some references call Lilium
michiganense Turk’s cap lily, a mix-up that shows why scientific names are
helpful. They may be tongue-twisters, but unlike common names, scientific names
are usually the same no matter where you are (or what you’re reading), so there’s
less confusion.
According to most references, this one is almost certainly
Michigan lily. It’s 3–4 feet tall, well within the 3– to 6–foot height typical of this
species. Turk’s cap lily tends to grow taller, usually 5–7 feet.
Their flowers also differ, but the differences are subtle. Both
species have umbels of nodding flowers with orange-red, dark-spotted tepals (similar petals and sepals) that are
reflexed, bending back toward the base of the flower. Large stamens and a long
pistil emerge from the center of the flowers and hang downward.
 |
| Umbels of Michigan lily flowers (left) and sets of whorled leaves on the stem (right). |
In Michigan lilies the tips of the tepals are said to reach
the base of the flower, but not much farther. In contrast, the tepals of Turk’s
cap lily reach so far back they go beyond the base of the flower and may touch
each other. In addition, their anthers, the pollen-bearing tips of the stamens,
differ in length. According to several references, those of Michigan lily are
never more than ½ inch long, whereas those of Turk’s cap lily are at least ½ inch
long or longer.
If you don’t have a ruler handy, there are other differences
to look for. If flower buds are present, look at their shapes. Michigan lily buds are more or less round in cross section, whereas Turk's cap lily buds are triangular. Open flowers also display differences. The pistil of Michigan lily is orange-red, whereas the pistil of
Turk’s cap lily is greenish white to whitish orange. Looking deep into the
flower, you’ll sometimes see a green, star-shaped center in Turk’s cap lily,
but not in Michigan lily.
Another look-alike is the
introduced tiger lily, Lilium lancifolium, a garden favorite. It differs
from both Michigan and Turk’s cap lilies in that it has alternate, not whorled,
leaves, and small bulbs in the leaf axils.
Growing near this Michigan lily was yet another look-alike, Tawny day lily, Hemerocallis fulva. Also called ditch lily for its common habitat, it has orange-red flowers that open upward and have streaked but not spotted tepals. Day lilies have strap-shaped basal leaves but no leafy stems.
 |
Tawny day lily flowers on leafless stems amid strap-shaped basal leaves. The flowers open upward, their red-orange tepals streaked but not spotted. |
Michigan lily ranges throughout the upper Midwest and the Great Lakes region and less commonly farther east and south. In this region, it flowers in July. Pollinators are thought to be hummingbirds, butterflies and moths.
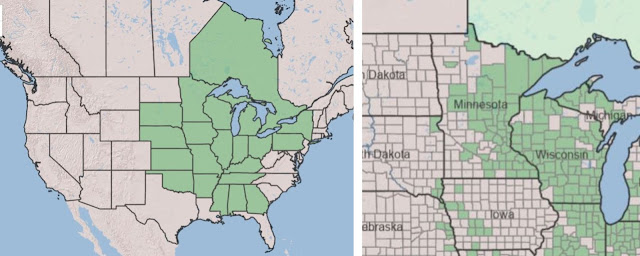 |
| Michigan lily's range in North America (left) and the Upper Midwest (right). Maps from USDA Plants Database. |
References
USDA, NRCS. 2023. The PLANTS Database
(http://plants.usda.gov, 07/18/2023). National Plant Data Team, Greensboro, NC
USA.



