 |
| Moonseed vine, Menispermum canadense, in early fall. Although most of its leaves have now fallen, it can still be identified -- and avoided, if foraging. |
Moonseed vine (Menispermum canadense), also called
Canada moonseed, is a twining vine of deciduous forests and riverbanks, thriving
in moist or mesic soils and partial shade. Although the vines have now shed their
leaves, moonseed vine can still be identified by other characteristics, and for
foragers of wild foods, the distinctions could be lifesaving.
The danger comes from mistaking moonseed vine for riverbank
grape (Vitis riparia). Both vines produce clusters of deep blue or
purple, spherical fruits that can remain on the vines through winter. Unlike
edible grapes, however, moonseed fruits are poisonous.
That’s because moonseed vine contains alkaloids, compounds many
plants produce for defense against herbivores. Although alkaloids have been and
are used medicinally, they can also be poisonous. Several sources report that
eating moonseed vine, especially the fruits and seeds, can be fatal because of its alkaloids. The Minnesota Poison Control System includes
moonseed on its list of toxic plants and advises calling Poison Control if any
part of the plant is eaten.
Fortunately, poisoning can be avoided. There are reliable ways to tell the difference between moonseed and riverbank grape, even in fall and winter. Here’s what to look for.
Moonseed is a twining vine. It clambers over other vegetation or climbs upward by wrapping its stems around small trees or shrubs. Riverbank grape is a grasping vine. It uses tendrils, modified leaves, to clutch onto supports and hold the vines upright.
 |
| Twining stems of moonseed vine, left, and grasping stems of riverbank grape, right. |
The young stems of moonseed vine are brown or greenish brown and hairy, although as the stems age, they lose the hairs. Stems grow as large as 2 cm in diameter ( a little less than an inch) and have ridged or fluted bark.
Younger stems of grapevine are brown or reddish brown and hairless. Mature stems grow up to 20 cm in diameter (about 8 inches) and have brown, shaggy bark. |
| Young moonseed stems, left, are brown or brownish green and hairy. Young stems of riverbank grape, center, are reddish brown and smooth. Mature stems of riverbank grape, right, are brown and shaggy. |
Leaf scars are marks on woody stems left by petioles when
leaves are shed in fall. Inside them are small, often raised dots called bundle
scars, created when strands of vascular cells (water- and food-conducting
cells) are severed when leaves fall off the stem. Buds – next year’s protected
growth – sit above the leaf scars.
The leaf scars of moonseed vine are typically 2-3 mm long
and wide, oval to circular in outline, and concave. They are often notched or
split at the top. Inside the leaf scar, the bundle scars are arranged in a
faint, broken circle or oval. The bud is barely visible above the leaf scar; it
appears to be embedded in the stem, protruding a millimeter or less above
the surrounding tissue.
 |
| Leaf scar and bud of moonseed vine viewed from the front (left) and side (right). |
The leaf scars of riverbank grape are typically 2-4 mm long and wide and roughly triangular, semicircular, or U-shaped. The perimeter of the leaf scar may be ridged, but the leaf scar is not noticeably concave. To the side of the leaf scars are linear marks called stipule scars.(Stipules are thread-like or leafy structures at the bases of petioles in some plants.) Bundle scars are hard to see, but there are several. The bud is brown or reddish brown and 3-5 mm long.
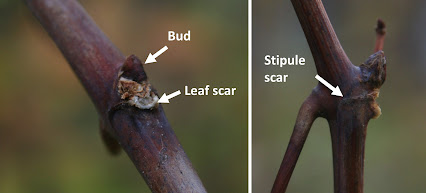 |
| Leaf scar, bud and stipule scar of riverbank grape viewed from the front (left) and side (right). |
Both moonseed vine and riverbank grape have alternate, lobed
leaves, but they have different margins (edges) and points of petiole attachment. These features can also be found on fallen leaves if they’re still
intact.
The margins of moonseed leaves are smooth, although the lobes may have pointed tips. In addition, the petioles are attached inside the leaf blade, even if just barely, making a peltate or shield-shaped leaf blade. The leaves of riverbank grape are sharply and coarsely toothed, and the petiole is attached at the edge of the blade, at its base.
 |
| Riverbank grape, left, has lobed, coarsely toothed leaves. Moonseed vine (right) also has lobed leaves, but the margins are smooth, not toothed. |
 |
| The petiole of riverbank grape, left, is attached at the edge of the blade. The petiole of moonseed vine, right, is attached just inside the blade. |
Although aboveground characteristics are enough to positively identify
moonseed and grapevine, belowground structures can also be helpful if it's possible -- and permissible -- to uncover or uproot them.
Moonseed vines have yellow rhizomes, underground stems that
grow horizontally and produce roots and shoots along their length. Because of their
color and traditional use to treat various ailments, Dakota Indians call it yellow
medicine, the namesake of Yellow Medicine River and Yellow Medicine County in
southwest Minnesota. The homeland of the Dakota is Pezihutazizi Kapi,
“the place where we dig for yellow medicine.”
No source for this article describes grapevine as having rhizomes, but its woody, brown stems can become buried and grow roots at their nodes. These rhizome-like stems look nothing like the slender, yellow rhizomes of moonseed vine, however.
 |
| The rhizomes of moonseed vine, left, are yellow. The roots and rhizome-like stems of riverbank grape, right, are brown. |
Moonseed vine is found in much of Minnesota but is more abundant in the southern part of the state. Its broader range generally covers the eastern half of the US. The vine flowers in late spring and early summer. For more information, see the webpages from Minnesota Wildflowers and The Friends of the Wildflower Garden, Inc. Both are linked below.
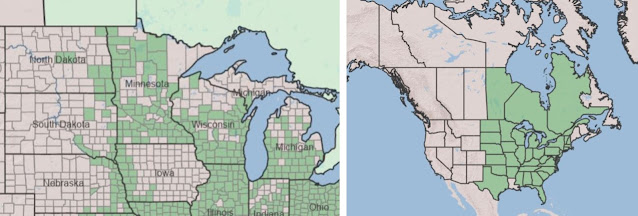 |
| Range maps of moonseed vine, from the USDA Plants Database. |
Riverbank grape is also found in most of Minnesota except
for several counties in the far north and northeast. More broadly, its range
extends from the Mid-Atlantic states into New England and west through the
Dakotas.
Friends
of the Wildflower Garden
University
of Wisconsin – Green Bay, Cofrin Center for Biodiversity Herbarium
Minnesota
Poison Control System
USDA, NRCS. 2023. The PLANTS Database
(http://plants.usda.gov, 10/14/2023). National Plant Data Team, Greensboro, NC
USA.




